Subtotal: $39.00
Lorazepam
$25.00
Lorazepam is a prescription benzodiazepine medication that is a central nervous system depressant. Its brand names include Ativan® and Loreev XR®. It is used to produce a calming effect by slowing down activity in the brain and nerves.
Category: Buy Sleeping Pills
Lorazepam increases the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a natural chemical in the body that reduces nerve activity. This leads to relaxation and reduced anxiety.
Tablet descriptions
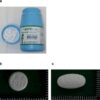
Lorazepam tablets are available in several strengths, which are indicated on the pill.
- Strengths: Tablets come in 0.5 mg, 1 mg, and 2 mg doses.
- Other forms: The medication is also available as an oral concentrate, extended-release capsules, and an injectable solution.
Common uses
Lorazepam is prescribed for the short-term relief of severe anxiety and for other specific medical purposes.
- Anxiety: Manages anxiety symptoms and anxiety disorders.
- Insomnia: Treats sleep difficulties caused by anxiety or temporary stress.
- Seizures: Administered via injection for certain seizure disorders, including status epilepticus.
- Sedation: Used as a sedative before medical procedures or surgery.
- Alcohol withdrawal: Helps manage symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
Important warnings
Lorazepam can cause serious side effects, including severe drowsiness, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms if discontinued abruptly.
- Addiction and dependence: Long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence.
- Withdrawal: Do not stop taking the medication suddenly without consulting a doctor, as it can cause serious withdrawal symptoms.
- Central nervous system (CNS) depression: Taking lorazepam with alcohol or other depressants (including opioids) can cause dangerous sedation, breathing problems, and even death.
- Impairment: It can cause drowsiness and unsteadiness. Patients should not drive or operate machinery until they know how the medication affects them.
Common side effects
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Unsteadiness or coordination problems
- Confusion
- Changes in appetite
Be the first to review “Lorazepam” Cancel reply
Related products
Sale!
Buy Sleeping Pills
Sale!
Buy Sleeping Pills

 Zopiclone
Zopiclone 


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.